Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep, which can lead to a variety of health problems. One of the most effective treatments for sleep apnea is the use of a mouth device, also known as an oral appliance or mandibular advancement device. These devices work by repositioning the jaw and tongue to keep the airway open during sleep. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of mouth devices, and their benefits, and provide tips on how to choose the right one for you.
Click this link https://highlandfamilydentistry.net/services/mouth-devices/ to know more about mouth devices. There are several types of sleep apnea mouth devices available, each with its own unique design and functionality. The most common types include:
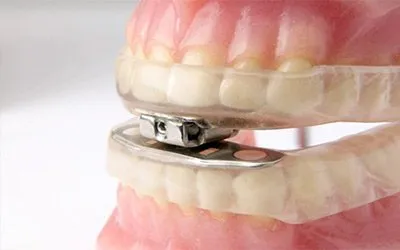
1. Mandibular Advancement Devices (MAD): These devices work by holding the lower jaw in a forward position, which helps to keep the airway open. MADs are custom-made to fit an individual’s mouth and are adjustable to provide maximum comfort.
2. Tongue Retaining Devices (TRD): TRDs are designed to hold the tongue in a forward position, preventing it from blocking the airway during sleep. They typically consist of a suction cup that attaches to the tip of the tongue and a mouthpiece that keeps the tongue in place.
3. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Devices: CPAP machines are the most common treatment for sleep apnea. They work by delivering a continuous flow of air through a mask worn over the nose or mouth. This air pressure helps to keep the airway open and prevent breathing pauses.
4. Oral Pressure Therapy Devices: These devices use a combination of negative pressure and positive pressure to keep the airway open. They consist of a mouthpiece that creates negative pressure to pull the soft tissues of the airway forward, while simultaneously delivering positive pressure to keep the airway open.